Home
Smart Government Strategy
Share The Page
The Smart Government Strategy (2020-2024) defines the Kingdom's aspiration, vision, objectives, initiatives, and action plan. Most strategic initiatives are geared towards achieving SDGs by taking actions and innovative approaches to align with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Saudi Vision 2030. The Strategy is also guided and aligned with the Saudi Vision 2030 goals and strategic objectives. The objective is to specify how the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia will deliver on its vision to digitally transform the Government and build world-class Smart Government capabilities.
The Smart Government Strategy sets an ambitious goal that, by 2024, the Government within the Kingdom will be Agile, Capable, and Innovative resulting in new seamless Smart Government experiences for the beneficiaries, centered around their needs. The Government aspirations include:
- Deliver a unified and world class smart service experience.
- Provide all public servants with leading smart capabilities.
- Equip leaders with insights to solve tomorrow's challenges today.
- Deliver the future through a digitally capable, inclusive workforce.
- Fast track digital through an ecosystem of partners.
- Make use of shared resources to deliver more for less.
To ensure consolidation of the identified considerations and opportunities, the Kingdom has defined its aspirations to build a unified leading Smart Government that evolves around its beneficiaries - citizens, residents, tourists, and businesses alike.
Vision
Based on the ambitions and aspirations of the Kingdom, the Vision of the Strategy carries four key components that articulate Saudi Arabia's Smart Government ambitions as outlined in Vision 2030.

Goals and Strategic Objectives
To achieve the Kingdom's aspirations and Vision, the Strategy defines four main goals and twelve strategic objectives.
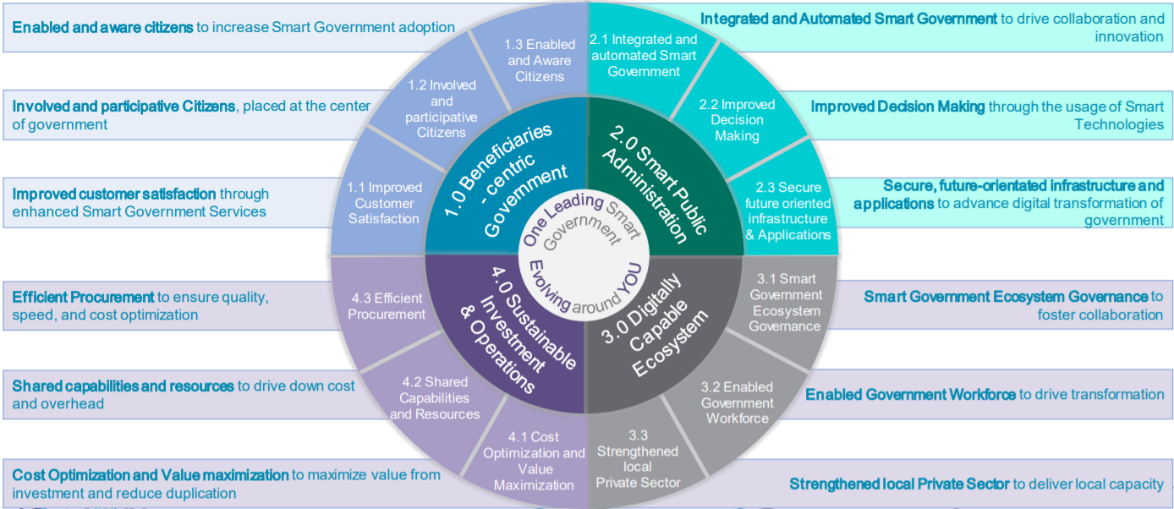
Goal 1.0: Beneficiaries – Centric Government
The offering of services to citizens and businesses in a targeted manner through their preferred channel, any time and any where, with the aim of delivering a rich and personalized experience that meets the needs of beneficiaries in the most intuitive way to them.
Strategic Objectives:
- 1.1 Improved Customer Satisfaction through enhanced Smart Government Services.
- 1.2 Involved and participative Citizens, placed at the center of Government.
- 1.3 Enabled and Aware Citizens to increase Smart Government adoption.
Goal 2.0: Smart Public Administration
Establishment of Smart Administration capabilities across Government to aid better decision making, design infrastructure and systems that meet the needs of a leading smart government, and increase efficiencies based on data insights, automation and streamlining of services, and reducing repetitive manual labor. The goal will also bring the Government closer together to ideate and innovate together on the basis of leading technology capabilities.
Strategic Objectives:
- 2.1 Integrated and automated Smart Government to drive collaboration and innovation.
- 2.2 Improved Decision Making through the usage of Smart Technologies.
- 2.3 Secure future-oriented infrastructure & Applications to advance the digital transformation of Government.
Goal 3.0: Sustainable Investment and Opportunities
Establishment of a Digital Ecosystem driving the digital transformation of Government and redefining the delivery of services through collaboration across the public and leading local private sector. This ecosystem is facilitated by a digitally capable workforce, strong processes to bring Government together and break silos and a robust market place with strong standards and controls, delivering expedited access to leading private sector capabilities.
Strategic Objectives:
- 3.1 Smart Government Ecosystem Governance and Regulation to foster collaboration.
- 3.2 Enabled Government Workforce to drive transformation.
- 3.3 Strengthened local Private Sector to deliver local capacity.
Goal 4.0: Digitally Capable Ecosystem
Establishment of an ICT investment framework to test requested budgets and projects on Return on Investment and Value and the sustainability of solutions. In line with this, emphasize is placed on the re-use of shared capabilities across Government with the aim to reduce duplication of efforts. This framework will be supported by robust procurement guidelines and project review stage gates, ensuring control and ongoing learning and optimization.
Strategic Objectives:
- 4.1 Cost Optimization and Value Maximization to ensure sustainability.
- 4.2 Shared Capabilities and Resources to drive down cost and overhead.
- 4.3 Efficient Procurement to ensure quality, speed, and cost optimization.
The Strategy contains an implementation Action Plan for operationalization of the initiatives, implementation timeline, critical success factors, mitigations for potential risks and the following steps to activate the strategy.
Drivers for Smart Government Transformation
The Strategy identifies three essential drivers for the Smart Government Transformation: National Drivers (Vision 2030, National Digital Transformation Strategy, and ICT Sector Strategy); Technology Drivers (Robotics & Automation, Internet of Things (IoT), Blockchain, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence (AI)); and, Socio-Economic Drivers (Social Media and Sharing, Mobile First, DIY & Self Service Culture, Sharing Economy, and Digital Identity and Trust).
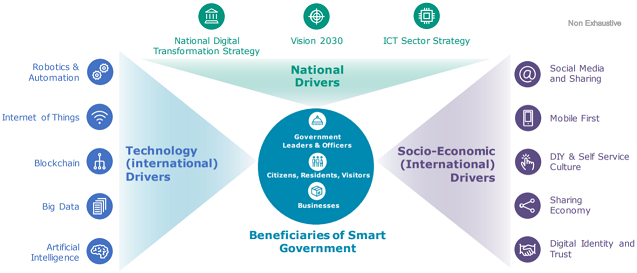
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are recognized as essential technology drivers for the Smart Government Strategy. The Strategy provides for using the Robotics & Automation, Internet of Things (IoT), Blockchain, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to achieve the Vision 2030 and Smart Government Strategy goals and objectives.
The Strategy makes reference to the adoption of Emerging technologies in four strategic objectives, each of them further operationalized by initiatives and projects.
Strategic objective 2.2: Improved Decision Making through the usage of Smart Technologies
- Initiative 2.2.1: Data Insights CoE: This imitative looks to establish a center of excellence, equipped with a Data Insights Advisory team, an effective scalable technology platform, and relevant frameworks, around the use of emerging analytics and cognitive technologies to drive data insights that can help government entities develop government policy or improve service delivery.
Projects:
- Data Insights Advisory Team: Establish a team of experts that can work with government entities to analyze internal and external data sources to answer specific questions. This team will be responsible for driving forward the Big Data and the Open data strategies, in addition to setting an Insight decision framework, and developing an Advanced Analytics Platform.
- Insight Decision Framework: Establish an approach and framework to redefine decision making practices and drive up the use of data for the purpose of making better decisions across government.
- Advanced Analytics Platform: Design and implement an advanced analytics platform that will power the analytics capabilities of the data insights CoE and provide the required advanced analytics and computing capabilities to produce meaningful insights.
Strategic objective 2.3: Design Secure, future-orientated infrastructure and applications to advance the digital transformation of Government
- Initiative 2.3.2: Open Innovation: This initiative aims to establish innovation communities of practices around one or more labs to Incubate new approaches to the delivery of Smart services, driven by a culture of innovation and sharing
Projects:
- Hackathons: Regular Hackathon events to explore new technologies and innovate across government. These events will be part of the Digital Government ecosystem, communicate schedule and tackle a range of topics, including Big Data, Blockchain, Open Data, Artificial Intelligence, and other topics.
- Blockchain Strategy: Development of a national Blockchain strategy.
- Open Innovation Platform: Develop a Digital platform that connects and matches real business challenges or digitalization opportunities of government entities or businesses (Problem Owners), to start-ups or tech firms (Problem Solvers), where challenges can be accompanied with prize monies for the best solutions that are selected based on the criteria of Problem Owners.
- Open Innovation Lab: Create a physical innovation lab to broker the opportunities to match business problems faced by entities with innovative solutions. This lab will focus on developing use cases for topics such as Blockchain, IoT, Big Data, and Artificial intelligence, etc.
Strategic objective 3.2 Enabled Government Workforce to drive transformation
- Initiative 3.2.1: Digital Workforce: This initiative aims to establish a clear view for national workforce planning, a national digital career framework, and establish a gender equality program, with the ambition to equip government with a diverse workforce, who have the capability and capacity to carry the Smart Government transformation. Additionally, this initiative is looking to establish a digital curriculum, providing training all public sector staff and select private sector on basic and advanced digital discipline, to ensure that a minimum level of digital skills and relevant advanced skills are present in all entities.
Projects:
- Digital Academy: Evolution of the existing Digital Academy to provide training courses for individuals engaged in transformation initiatives. This training will focus on the deep technical skills government employees require to undertake their roles in specific transformation projects. This Academy will also include emerging technologies-related courses, such as Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, IoT, Blockchain, etc.
- Curriculum Development: Work with education providers to ensure the necessary ICT skills are taught to students to uplift the digital capabilities of the Saudi public. This would include setting curriculums for Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and other emerging technologies relevant topics.
Strategic objective 3.3 Strengthened local Private Sector to deliver local capacity
- Initiative 3.3.1: Local Capacity Building: This initiative targets to strengthen the local private sector and improve its ability to innovate, by establishing communities of preferred suppliers that receive early insight into long terms strategies and future initiatives, promote innovation through competition and grands, and establishing a platform to match public sector problems with innovators
Project: Vendor Communities: Establishment of communities of suppliers in order to:
- Brief vendors on the aims, outcomes and progress in delivering the Smart Government Strategy.
- Ensure vendors are aware, contribute and adopt the latest technical standards, policies and roadmaps for Government Products.
- Increase domestic vendor capacity and capability in areas where the market does not currently fully meet the government's requirements e.g. Artificial Intelligence. These communities will be used to discuss the challenges and provide insight into future government procurements, enabling local vendors to improve their capability and capacity ahead of demand reaching the market.
- Innovation Grants: Provision of innovation grants to spur the local market to grow their capabilities and capacity in areas w here government demand can still not be met, supporting local companies to develop innovative products or services. Provision of grants will be via a competitive process to ensure maximum value for the country.
- Consolidate Data Centers: Optimization of government data centers and migration to the Cloud.
Read more about the Legal framework for Digital transformation , Emerging technology projects , Foresight Tools , and Regulatory sandbox .
E-Participation and Digital Inclusion
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia makes all necessary efforts to ensure digital inclusion for all its citizens and residents, including vulnerable groups such as people with disabilities, women, youth, elderly, immigrants, etc. For that purpose, the Kingdom has already joined a number of international conventions.
The question of digital inclusion and leaving no one behind is among the top priorities of the Saudi Vision 2030. The third pillar, "An ambitious nation," directly refers to the benefits and needs of the digital transformation and the need for digital inclusion of all Saudi citizens and residents. Moreover, as a Vision Realization Program, the National Transformation Program identifies several objectives directly focused on the digital inclusion of all citizens, including vulnerable groups. These objectives include:
- Objective 13: Foster values of equity & transparency.
- Objective 14: Improve the quality of services provided to citizens.
- Objective 23: Develop the e-Government.
- Objective 34: Strengthen the Communication Channels with Citizens and Business Community.
The ICT Sector Strategy also addresses the importance of digital inclusion. The Second theme, "Increase local content," directly refers to the need for advanced technology and digital knowledge and awareness among citizens and residents. It also highlights the need for increasing female participation in the ICT sector.
The Smart Government Strategy addresses digital inclusion more specifically in Strategic objective 1.3. Enabled and aware citizens to increase Smart Government adoption. The Strategy looks to increase citizens awareness, access, and use of Smart Government services byThe eParticipation and Digital Inclusion are among the most significant priorities identified in Vision 2030 and the Smart Government Strategy.
To improve the overall eParticipation environment, the Strategy defines the Strategic objective 1.2. Involved and participative Citizens. For this purpose, the Strategy looks to increase the involvement of citizens by placing them at the center of Government by engaging them in service design and policy-making through:
- Involving Citizens through Digital consultation on future government legislation and regulation; and,
- Expanding the Open Data provision, better informing the public and supporting research and the development of new innovative products and services developed in the private sector.
The Strategy outlines two initiatives for operationalizing the Strategic objective 1.2:
- 1.2.1 Open Data: this initiative is looking to migrate more data onto Data.Gov.Sa, and establish communities of practice around building solutions, utilizing this data; to increase the availability and adoption of open data by citizens and businesses and use in community initiatives, research, innovation and development of new products and services; and,
- 1.2.2 Active Citizenry E-Participation: Building on existing surveying and polling functionalities, as present in Watani and Ma3an, this initiative looks to deploy and promote e-consultation functionality across Government to increase participation in policy-making and service development.
Data Governance
The National Data Governance is one of the priorities identified in the Smart Government Strategy. Specifically, Strategic objective 2.2: Improved Decision Making through the usage of Smart Technologies looks to unleash the potential within the data held by the Government to transform how the way Government operates and increase the quality of services provided to citizens. To enable this, the Smart Government Strategy focuses on:
- Establishing an insights framework and central team, equipped with the latest analytics tools, to develop insights from data held by the Government, which will drive better decision making; and,
- Establishing and rolling out Data Governance to improve the quality and sharing of data across the Government.
The Strategy defines one initiative for operationalizing the strategic objective:
- 2.2.2 National Data Management: It aims at formulating and democratizing mandatory frameworks and agreements that will standardize the approach to data management practices, ensuring data is maintained in line with leading practices, establishing and easing data sharing across government entities through national data governance data sharing, and management frameworks.
Collectively these must comply with National Cyber Security, Privacy and Data Protection legislation, and the national standards for interoperability.
Digital Identity
Saudi Arabia has already established digital identity as one of the eGovernment key enablers. All Saudi citizens and residents can create their Digital Identity (or electronic ID) by registering on the National Single Sign-On system developed by the National Information Center and the Ministry of Interior. They can use their digital ID for accessing more than 700 government online services available on my.gov.sa, other government portals, and services provided by third parties such as banks, telecom operators, etc. For more information on creating and using citizen's eID, please visit the National Information Center.
Recognizing the importance and the potential of the national digital identity, the Smart Government Strategy makes direct reference in the Strategic objective 1.1: Improved customer satisfaction through enhanced Smart Government Services. The aim is to ensure that citizens trust all government services and that their data is managed securely through a single common identity service, making digital services more secure and easy to use and enriching/automating these services by joining up the information provided by citizens through this standard digital identity across Government. The strategy defines two initiatives for operationalizing the Strategic objective 1.1:
- 1.1.2 National Portal: This initiative looks to improve the user experience, content representation and quality, as present on gov.sa, enrich its functionality, roll out different channels moving closer to the ambition of establishing My.Gov.Sa as a leading platform and one-stop-shop for all government information and most transactions.
- 1.1.3 National Identity and Trust: Utilizing the IAM and SSO capabilities, as present in Absher, the digital citizen ID, as established by the Ministry of Interior, and the work done by National Information Center around eSignatures and identity (non-human based identity), this initiative looks to mainstream identity and trust capabilities, introduce controls for citizens to take ownership of their data and unify the approach to identity and access the Government.
Digital-by-Default
The Saudi Arabia Government pursues a Digital-by-Default approach and aims to set up the digital communication channel as a primary by 2024 while utilizing traditional channels for those who either do not have access to the internet, do not have the relevant skills, or are in a unique situation requiring specific assistance. This means that alternative challenges will remain for assistance for particularly for users at risk of marginalization and digital exclusion.
The high level of internet penetration with approximately 98% of the population covered with 4G, with plans to have more internet coverage by 2024 and assuming a relatively high individual internet users percentage (83%), allows the Government to move the focus toward implementation of the digital by default" approach and "mobile-first" strategy. Both are identified as key priorities that can be implemented in the provision of governmental services by 2024.
Recognized as one of the drivers for Smart Government Transformation, the Smart Government Strategy provides for the adoption of a Mobile-First Strategy. The Strategy should be comprehensive, identifying required policy, process, regulatory, capability, architectural, application and infrastructure aspects needed to be put in place to establish a mobile-first approach for all KSA public sector to follow. This approach should ensure that content (while not mobile only) allows for content and services to be served via channels most used by Saudi citizens and residents.
Once Only Principle
The Once-Only Principle is recognized as one of the essential elements of the Smart Government Strategy. It is an eGovernment principle that aims to ensure that citizens and businesses only have to provide certain information to the government authorities only once (also known as a "Tell us Once Principle").
The Once-Only Principle is part of Strategic objective 1.1: Improved customer satisfaction through enhanced Smart Government Services. The aim is to ensure that citizens trust all services and that their data is managed securely through a single common identity service, making digital services more secure and easy to use and enriching/automating these services by joining up the information provided by citizens through this standard digital identity across Government, meaning that citizens only have to tell the Government once ("tell us once principle").
To operationalize the Strategic Objective, the Initiative: 1.1.1 Digital Engineering CoE leverages the capabilities present on My.Gov.Sa, the life experience framework, and the work done around the Service Design toolkit. This initiative sets up a Center of Excellence. Furthermore, it progresses KSA's journey towards beneficiaries centric and leading service delivery by implementing ten life experiences. More specifically, the initiative defines seven projects, such as Service Design Toolkit; Digital Engineering Center; Mobile-First Strategy; Customer Satisfaction; Citizen Centric Journey Development; User Experience Lab; and Digital Service Testing Framework.
Alignment with the UN SDGs
The current Smart Government Strategy (2020-2024), same as the Saudi Vision 2030, is guided by the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Most strategic initiatives are geared towards achieving SDGs by taking actions and innovative approaches to align the 2030 Agenda and the Saudi Vision 2030. The Strategy Themes and Aspirations have been directly linked to four SDGs:
SDG 1: No Poverty:
- Target: By 2030, ensure that all men and women, in particular the poor and the vulnerable, have equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to basic services, ownership and control over land and other forms of property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technology and financial services, including microfinance.
- KPI: Proportion of population living in households with access to basic services.
TAP Theme:
- Citizen and Business-centric Government
- Smart Public Administration
TAP Aspirations:
- Equip leaders with the insights to solve tomorrow's challenges today.
- Deliver a unified and leading smart service experience.
SDG 4: Quality Education
- Target: By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship.
- KPI: Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills, by type of skill.
TAP Theme:
- Citizen and Business-centric Government
- Digitally Capable Ecosystem
TAP Aspirations:
- Fast track digital through an ecosystem of partners
- Provide all public servants with leading capabilities
- Deliver the future through a digitally capable, inclusive workforce
SDG 5: Gender Equality
- Target: Enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology, to promote the empowerment of women.
- KPI: Proportion of individuals who own a mobile telephone, by sex.
TAP Theme:
- Citizen and Business-centric Government
- Digitally Capable Ecosystem
TAP Aspirations:
- Deliver the future through a digitally capable, inclusive workforce
SDG 17: Partnership for the Goals
- Target: Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms, in particular at the United Nations level, and through a global technology facilitation mechanism.
KPI:
- Number of science and/or technology cooperation agreements and programs between countries, by type of cooperation
- Fixed Internet broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants, by speed
TAP Theme:
- Digitally Capable Ecosystem
TAP Aspirations:
- Fast track digital through an ecosystem of partners.
Other SDGs addressed by the Strategy include SDG 9 (Industry, Innovations, and Infrastructure), SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions).
Alignment with the National Development Plans
The current Smart Government Strategy is guided and aligned with the Saudi Vision 2030 goals and strategic objectives. The purpose of the strategy is to specify how KSA will deliver on its vision to digitally transform the Government and build world-class Smart Government capabilities, in line with the Vision 2030 goal for Smart Government.
The Smart Government Strategy is also critical to the success of several Vision Realization Programs (VRPs), such as the National Transformation Program, Quality of Life Program, National Industrial Development and Logistics Program, and Housing Program. The demands from the VRPs (over 170 initiatives are linked with Smart Government) are extensive. The need to improve government services, provide shared platforms, develop standards and regulations, and improve decision-making is amongst the key needs. All VRPs are aimed to operationalize the Vision 2030 strategic objectives.
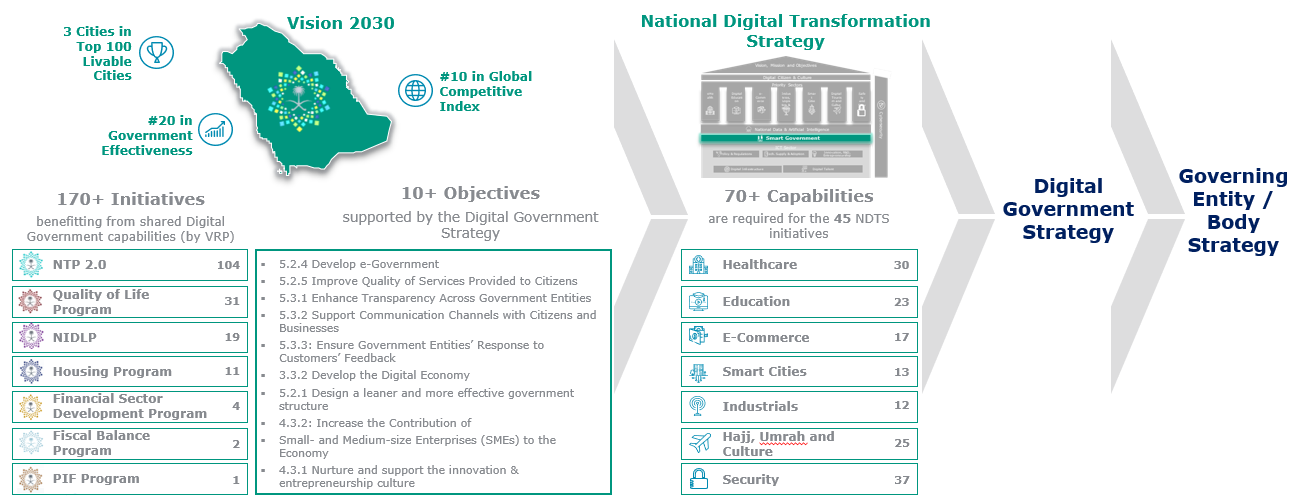
Alignment with the ICT Sector Strategies
The Smart Government Strategy is also fully aligned with the other key ICT sector strategies, such as the ICT Sector Strategy, National Strategy for Data & AI, Cyber Security Strategy, Cloud First Policy, Digital Health Strategy.
The Strategy (also referred to as an eGovernment Third Action Plan) plays a vital role in the National Digital Transformation System (NDTS) in the Kingdom.
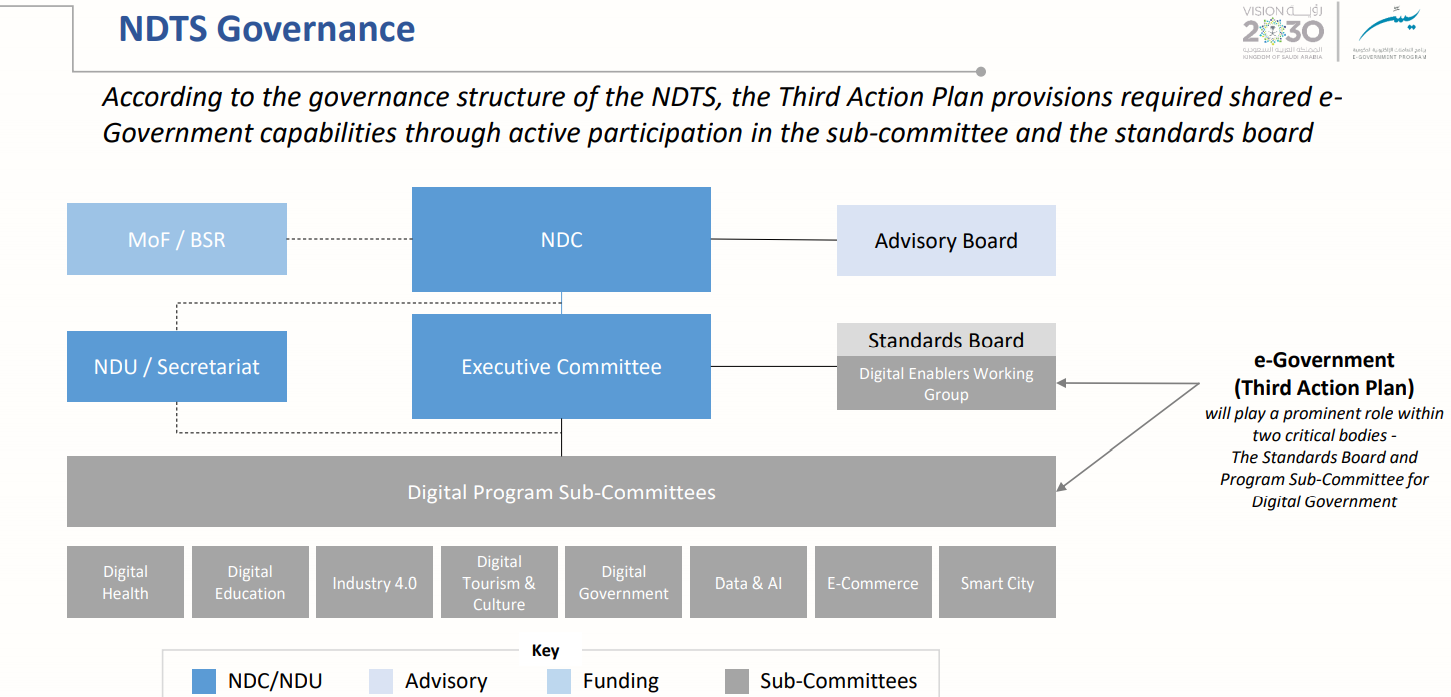
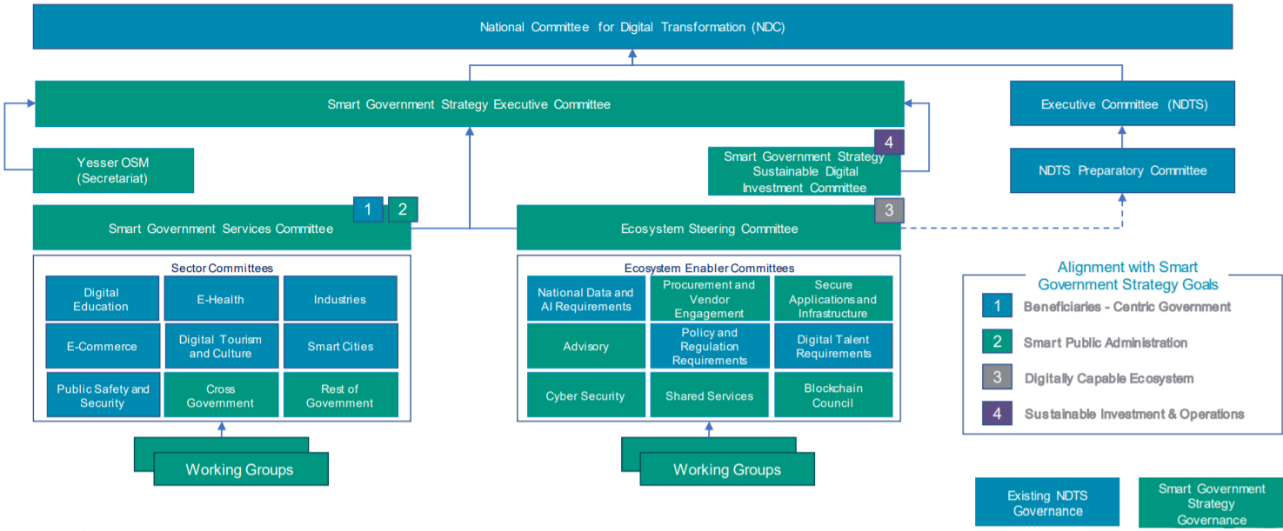
Implementation Governance Model
The Smart Government Strategy will be executed by a clear Governance Model that leverages NDC structures and is aligned with the Smart Government Strategy goals.
Comments & Suggestions
For any inquiries or comments, please fill in the required information.
Loading...

